
Telephone consultation
400-102-3850
Fine chemical industry
Production of Acetonitrile by Ammoniation of Acetic Acid
Background technology
The main use of acetonitrile is used as a solvent, such as as extraction of butadiene, isoprene extraction agent, synthetic fiber spinning solvent and some oil, phenol and colored substances solvent; in the oil industry used from animal and vegetable oil extraction fat solvent; in medicine for steroid drugs recrystallization reaction medium. Acetonitrile is also an intermediate of medicine (vitamin B1) and spices, and is a raw material for preparing 2-methylpyridine, triazine, ethylamines, dipropionitrile, imidazole, propylene bis acetonitrile, etc.
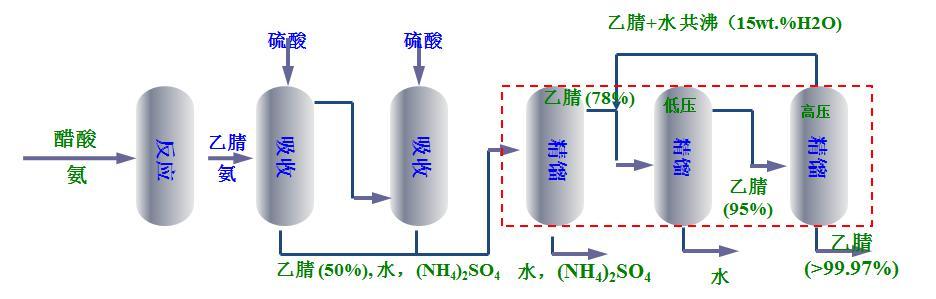
In the traditional process of synthesizing refined acetonitrile by the ammoniation of acetic acid, the acetic acid and ammonia gas are vaporized and then put into the reactor, and the ammoniation reaction occurs under the action of the catalyst with aluminum oxide as the carrier to obtain acetonitrile. After the reaction, the crude product body contains acetonitrile, water and a small amount of ammonia gas. After the two-stage absorption tower absorbs and removes ammonia gas, it enters the concentration tower, the negative pressure tower and the positive pressure tower in turn to obtain the finished product acetonitrile.
Since acetonitrile and water will form azeotrope (the water content of acetonitrile-water azeotrope at atmospheric pressure is about 16 wt.%), the acetonitrile mother liquor in the absorption section cannot be directly refined into finished acetonitrile by regular distillation (the water content of refined acetonitrile is usually ≤ 0.1 wt.%). At present, one concentration tower, one negative pressure tower and one positive pressure tower are mostly used for the refining of acetonitrile in the process of ammoniation of acetic acid to synthesize acetonitrile. This type of process has large steam consumption, large equipment area, long process flow, large feed liquid circulation, complex operation and low acetonitrile yield.
traditional process
new process
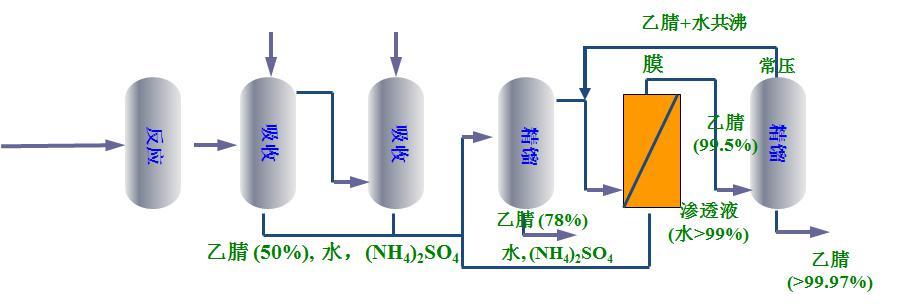
Technical advantages
The new process developed by Jiutian Gaoke has high recovery rate, simple process, high safety factor, high energy utilization rate, small material liquid circulation amount, low operation energy consumption (steam consumption of traditional process is 4 t/t, new process is 1.6~2 t/t), and no third component is added.
engineering case
Shandong Huihai, Nantong Liyang
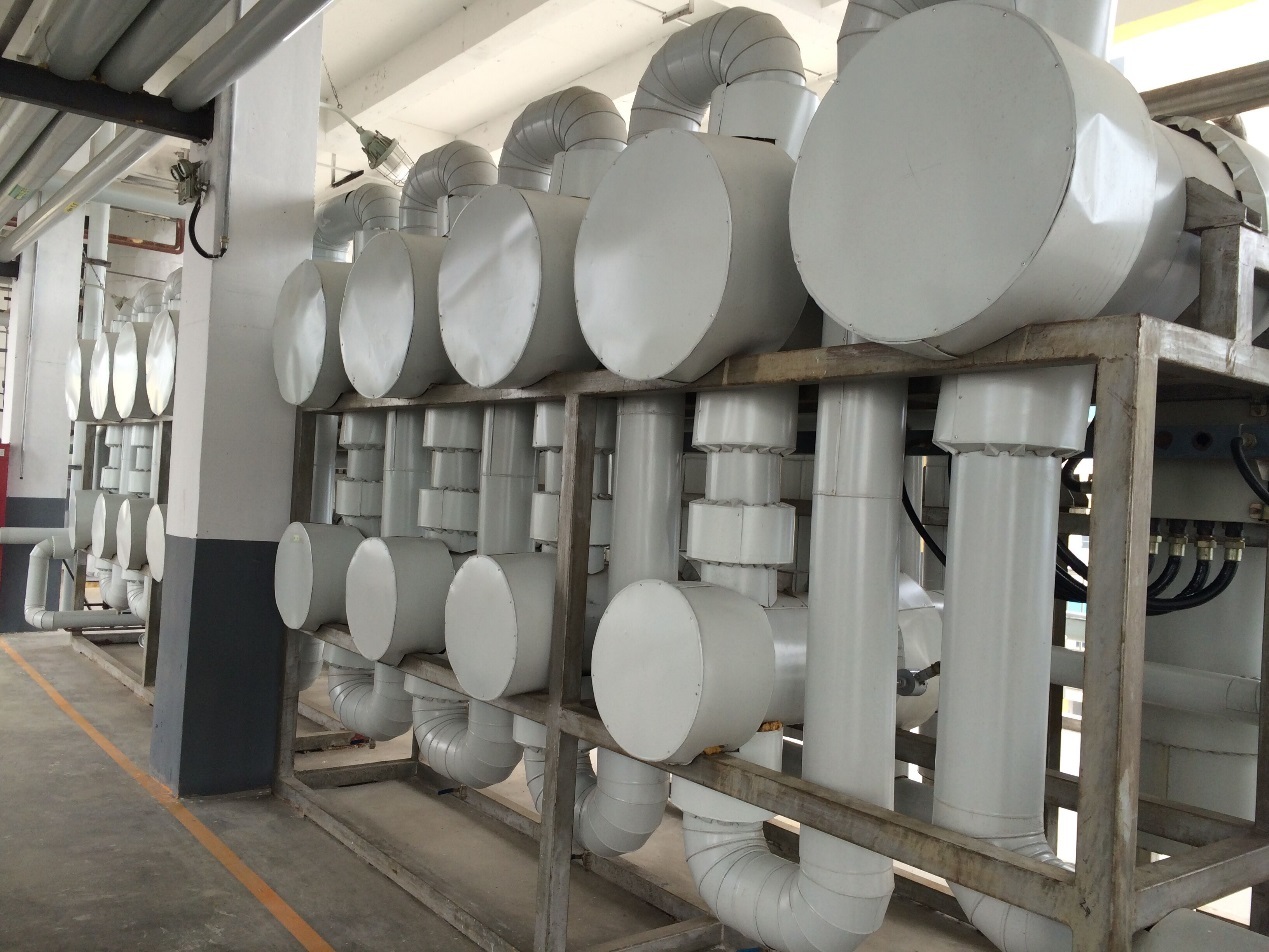

Shandong Huihai 10000 t/a acetonitrile plant
Production of isopropanol by hydrogenation of acetone
Background technology
Isopropanol is an important chemical product and raw material, which is widely used. China is the largest importer of isopropanol in Asia. At present, the annual output of isopropanol in China is about 160000 tons. As the production of isopropanol is restricted by many factors such as raw material supply, production process, environmental protection and so on, the domestic annual output is far less than the annual market demand. In 2010, the import volume of isopropanol was 115000 tons, and in 2011, the import volume of isopropanol was 100000 tons. Propylene direct hydration method is the main method of industrial production of isopropanol, it is to make propylene in the presence of a catalyst directly hydration reaction to produce isopropanol, while by-product n-propanol. Due to the shortage of domestic propylene resources, the propylene consumption and energy consumption of propylene hydration process to produce isopropanol are very high, and the production cost is very high. Contrary to the case of propylene, the domestic acetone production capacity is large, the market volume is rich, the price is low. Industrial acetone is almost always obtained by cumene peroxide (co-production with phenol). Due to the increase of the demand of phenol, a large amount of acetone is produced, and the imbalance of demand often leads to the situation of excessive acetone, which makes the price of acetone lower than the price of isopropanol and propylene. The development of acetone hydrogenation technology to produce isopropanol has broad application prospects.
The hydrogenation of acetone to produce isopropanol is accompanied by a small amount of side reactions, and the side reaction products mainly include water, diisopropyl ether, diacetone alcohol and 4-methylpentanol, etc. These by-products need to be separated in the subsequent purification process of isopropanol. Isopropanol purification generally uses two rectification columns for separation operations. In the first column, the by-product water and a small amount of unreacted acetone are removed at the top of the column, isopropanol and other heavy components are obtained at the bottom of the column, isopropanol products with a water content of <0.03wt.% are obtained at the top of the second column, and the remaining heavy components are removed at the bottom of the column. Because isopropanol forms a ternary azeotrope with water and acetone (acetone 8wt.%, isopropanol 81wt.%, water 11wt.%), the traditional dehydration and separation processes such as azeotropic distillation and extractive distillation are complicated in operation, high cost and serious environmental pollution, so that the current manufacturers generally sell them as waste liquid, resulting in a decrease in isopropanol yield and high production cost.
Production process
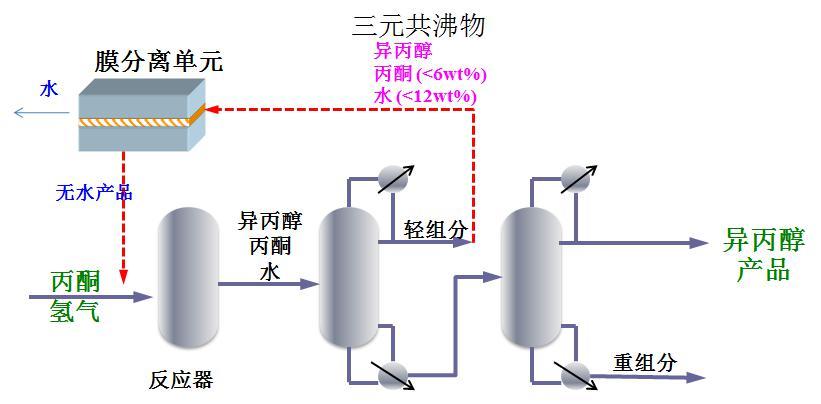
typical engineering case
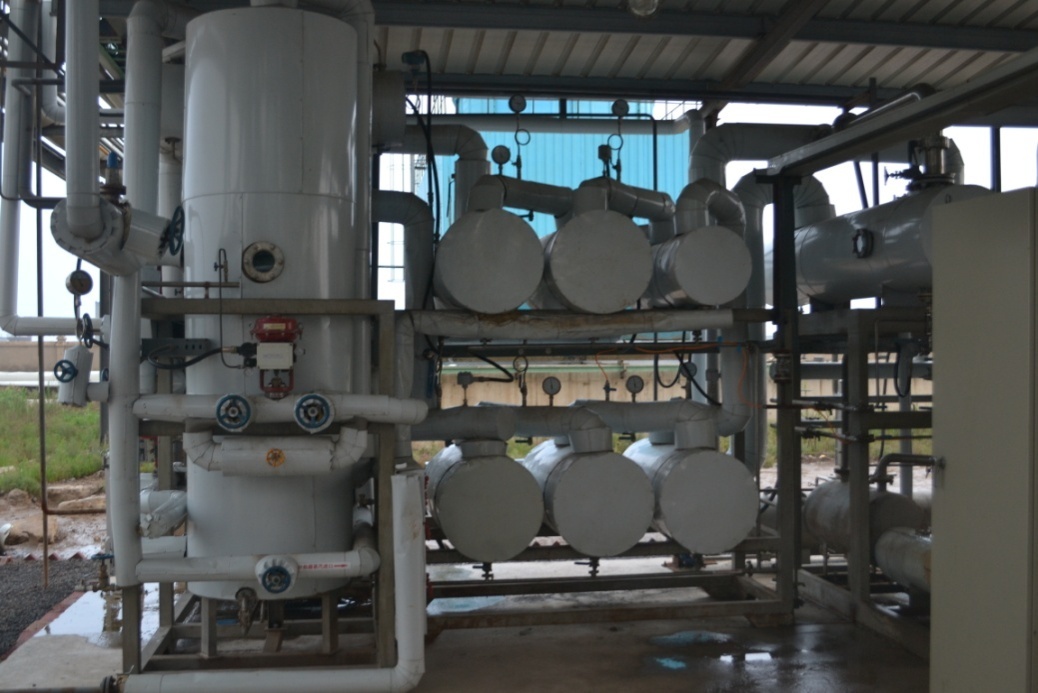

Yancheng Supur Chemical 8000 Tons/Year Isopropanol/Acetone/Water Membrane Plant








